Excerpted from the book, “What Goes on Inside a Wolf Pack”.
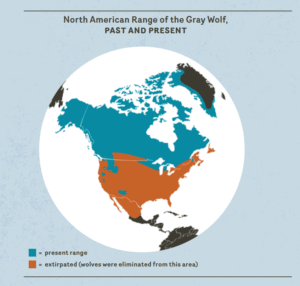
As wolves and coyotes expand their ranges in North America and individual animals migrate to new areas, more people may need to distinguish between the two species.
If you find yourself asking, “Was that a wolf?” check the range map to see if you live near wolf range. If you do, use the following guide to identify whether the animal was a wolf or a coyote.
If you have confirmed that both coyotes and wolves can be found at the observation site, here’s a guide that might help you identify if what you saw or heard was a coyote or a wolf.
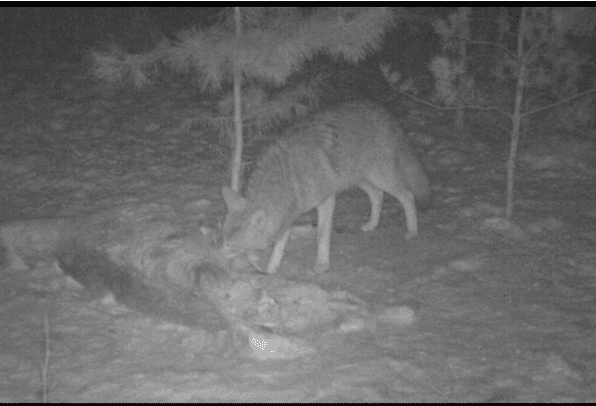

Trail camera image provided by Dave Haggard.
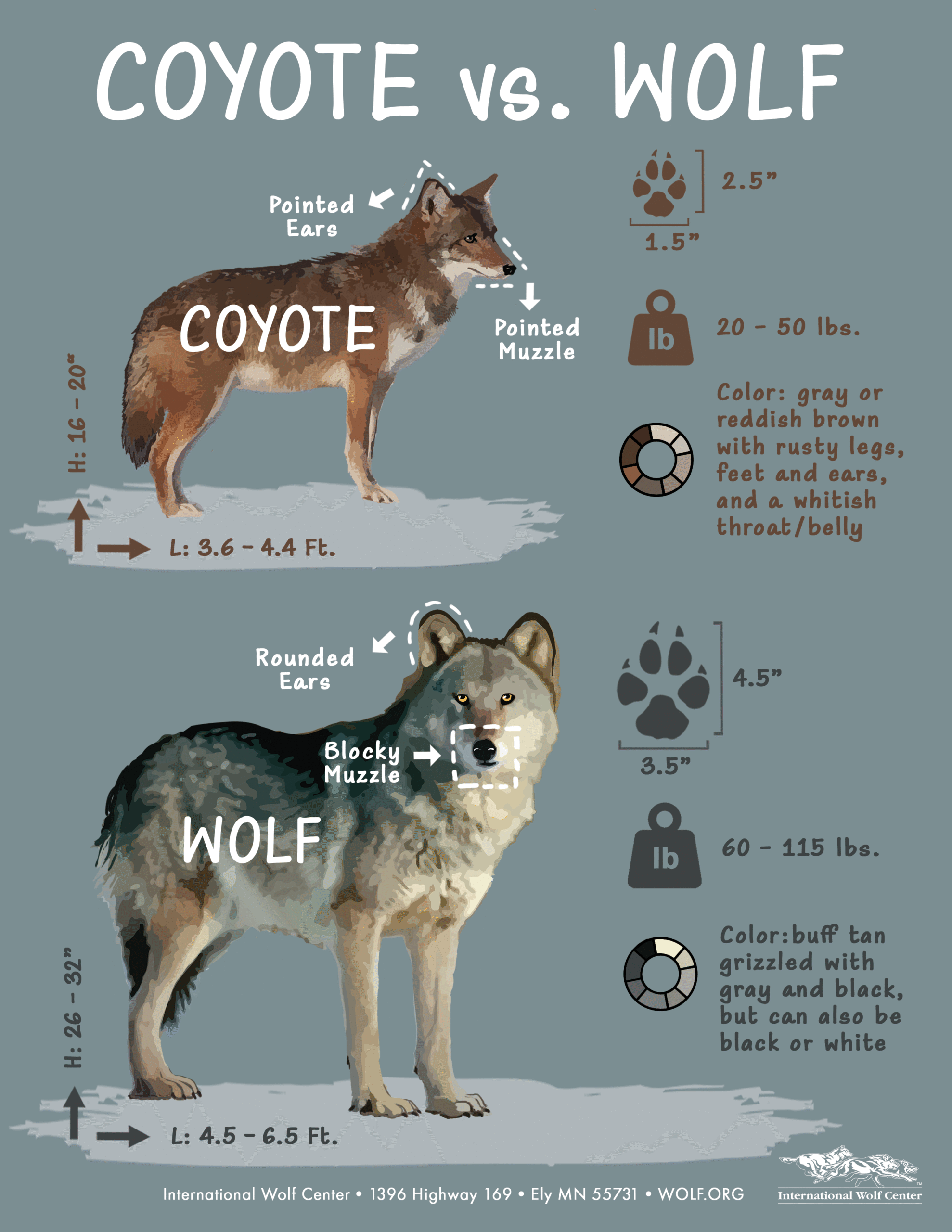
| Coyote | |
|---|---|
| Size | Height: 16-20 inches Length: 43-53 inches Weight: 20-50 pounds |
| Legs and Paws | Short legs relative to body size; paws are small and narrow |
| Ears | Large ears relative to head size with pointed tips |
| Face | Muzzle is narrow and pointed; head is small and triangular |
| Tracks | 2.5 inches tall, 1.5 inches wide |
| Coat Coloration | Gray to reddish brown with rusty legs and ears, and a light throat and belly |
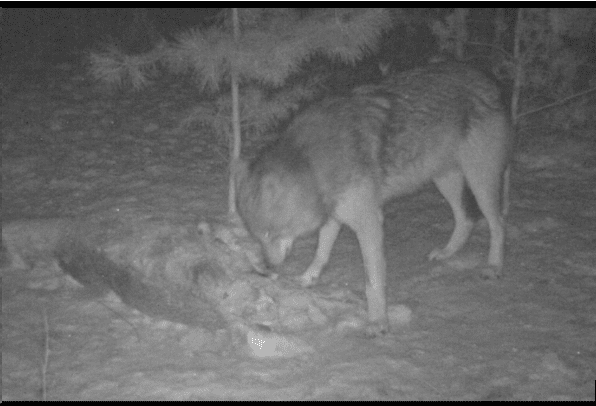

Trail camera image provided by Dave Haggard.
| Gray Wolf | |
|---|---|
| Size | Height: 26-32 inches Length: 54-78 inches Weight: 60-130 pounds |
| Legs and Paws | Long legs relative to body size; paws are large and robust |
| Ears | Small ears relative to head size with rounded tips |
| Face | Muzzle is broad; head is large and blocky |
| Tracks | 4.5 inches tall, 3.5 inches wide |
| Coat Coloration | A wide variety of colorations including gray, tan, black, and white |
Behavioral Differences between Wolves and Coyotes
In addition to physical differences, there are behavioral differences that might help you distinguish between a wolf and a coyote.
The way they move: A coyote’s walk is light-footed and bouncy, while a wolf has a smooth, deliberate stride. Both may trot, lope, and gallop. Although both species may live in family groups, coyotes are more frequently seen traveling and hunting alone or in pairs.
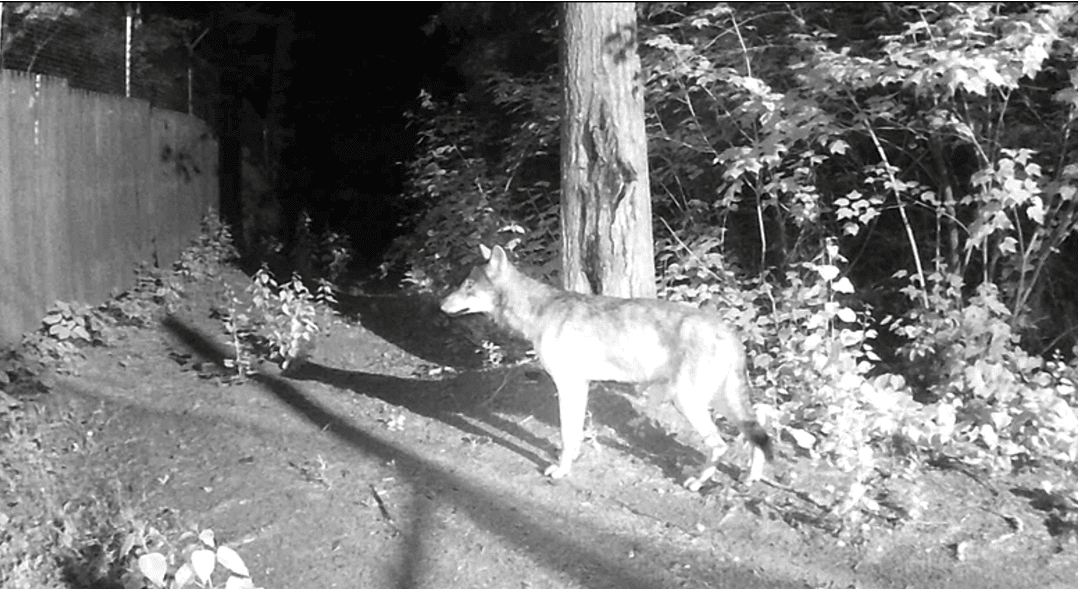
Wolf caught on a trail camera during the summer.
Coyote caught on a trail camera during summer.
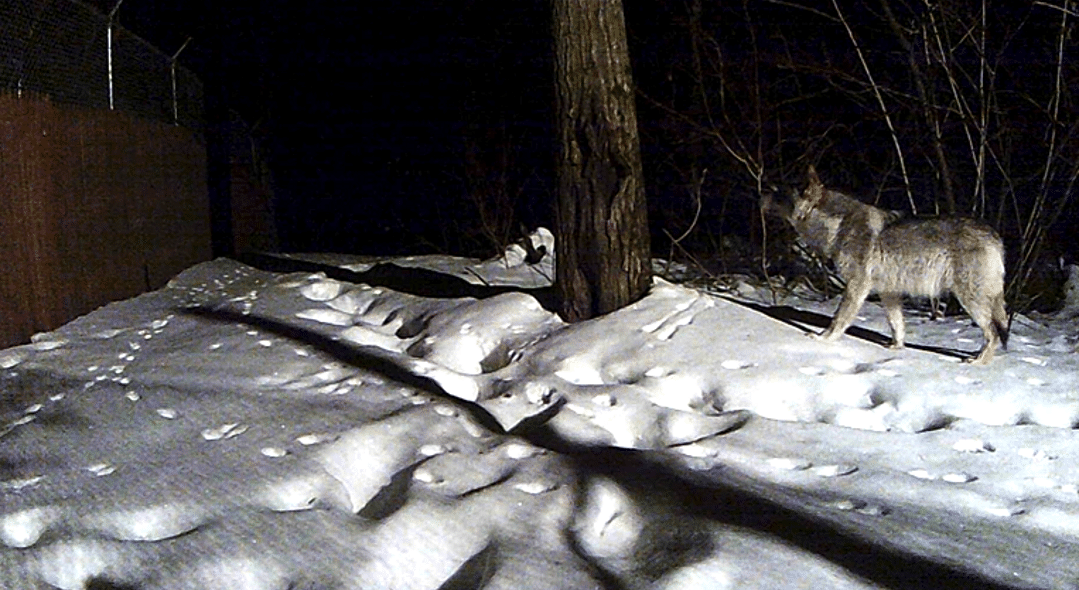
Wolf caught on a trail camera during the winter.
Coyote caught on a trail camera during winter.
The way they sound: In comparison to wolves, coyotes’ vocalizations are higher-pitched and shorter. Coyote vocalizations are typically described as “yippy”, and will often be heard with a variety of barks and yelps. A wolf’s howl is lower-pitched and longer. Wolf pups may be heard from late spring to early fall, resulting in some higher-pitched vocalizations as well. Wolves and coyotes may growl, bark, whine, and yelp.
The habitat they live in: Coyotes can be found in a variety of habitats, including urban areas. Wolves are also habitat generalists, but they reside in more rural areas with larger territories.
The food they eat: A wolf’s main diet consists of ungulates (large, hooved mammals like deer), but they also hunt smaller prey (such as rabbit/hare or beaver). Coyotes are opportunistic omnivores, meaning they eat whatever is currently available; however, their primary diet consists of meat. They hunt smaller mammals (such as rabbits/hares or rodents), but will also consume insects, amphibians, fish, fruits, and grasses. Both species scavenge on carrion (animal carcasses), but in most cases, it is more common with coyotes.
Download Coyote vs. Wolf flyer
(Imperial measurements) (Metric measurements)
Was that a Wolf or Dog?
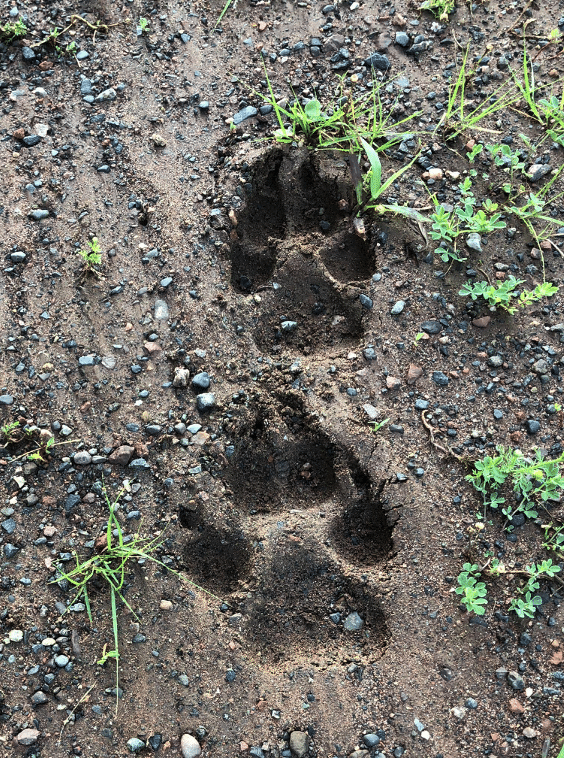

Wolf tracks in mud.
Domestic dogs have a wide range of sizes, shapes, and colorations. However, most dogs have smaller paws, broader chests, and patterned coat colors. Wolves look disproportionately lankier with larger heads compared to most dogs.
Tracks
Domestic dog tracks vary significantly in size, but the majority of dogs have smaller paws than a wolf’s. The toes of a dog’s paw splay outward, making the track appear more circular in shape. A wolf’s track tends to be more rectangular with the toes pointing forward.
In addition to physical differences, there are behavioral differences that might help you distinguish between a wolf or a domestic dog.
The way they move: Dogs have an indirect register to their stride, meaning that tracks from their hind feet often land slightly inside the tracks from their front feet. They will also wander and meander more often than wolves. To move more efficiently, wolves are also more likely to have a linear set of tracks and are more purposeful in their movements. Wolves have a direct register to their stride, meaning that their hind feet tend to fall directly in the tracks left by their front feet.
The way they sound: Wolves typically howl in low, prolonged tones. Barking for wolves is reserved for severe threats and serves as an alarm for the rest of the pack. Dogs may bark for any reason, and they have a wider range of vocalizations associated with different breeds of dog.
Seasonal Differences of Wolf and Coyote
Coyote - Winter
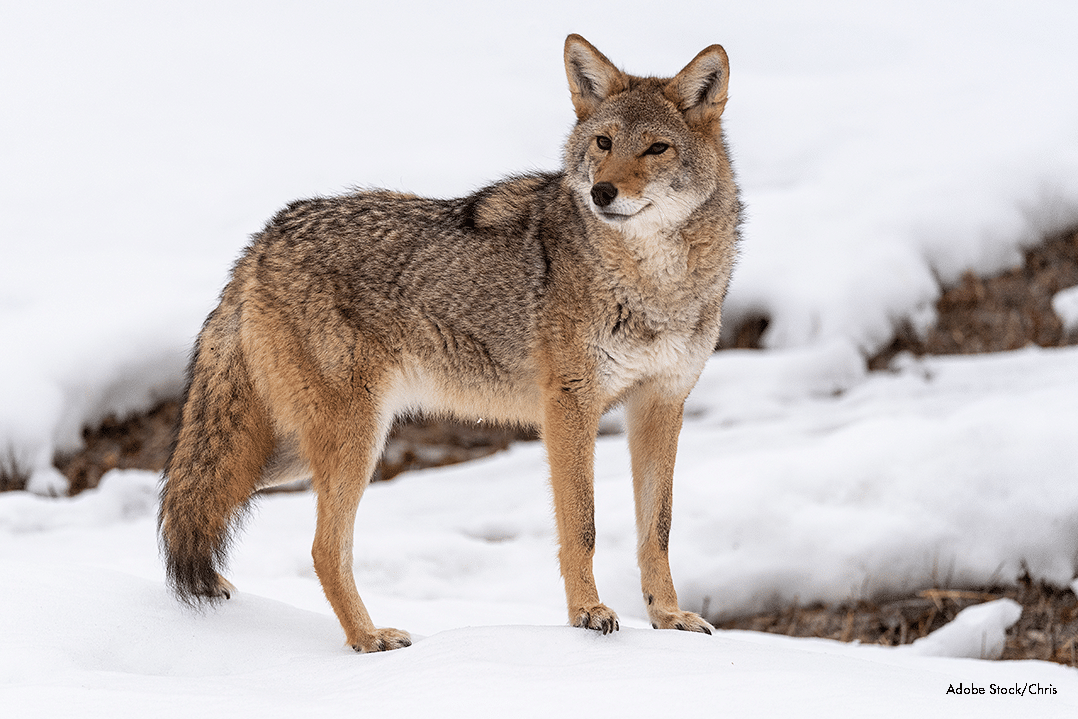
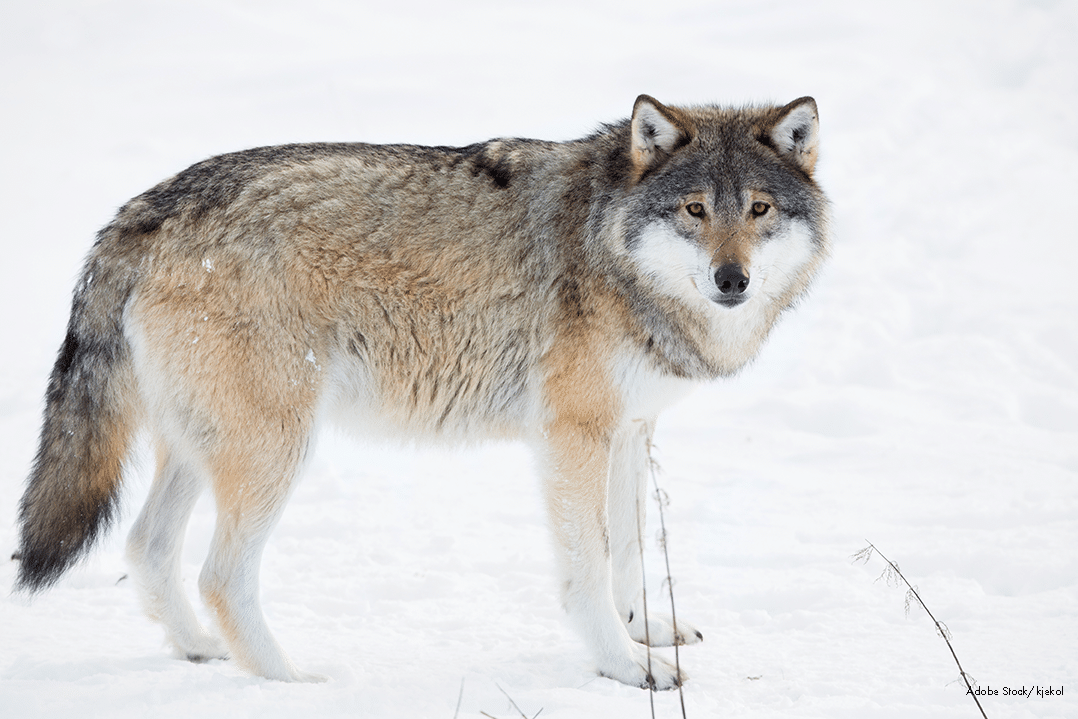
Gray Wolf - Winter
Coyote - Fall
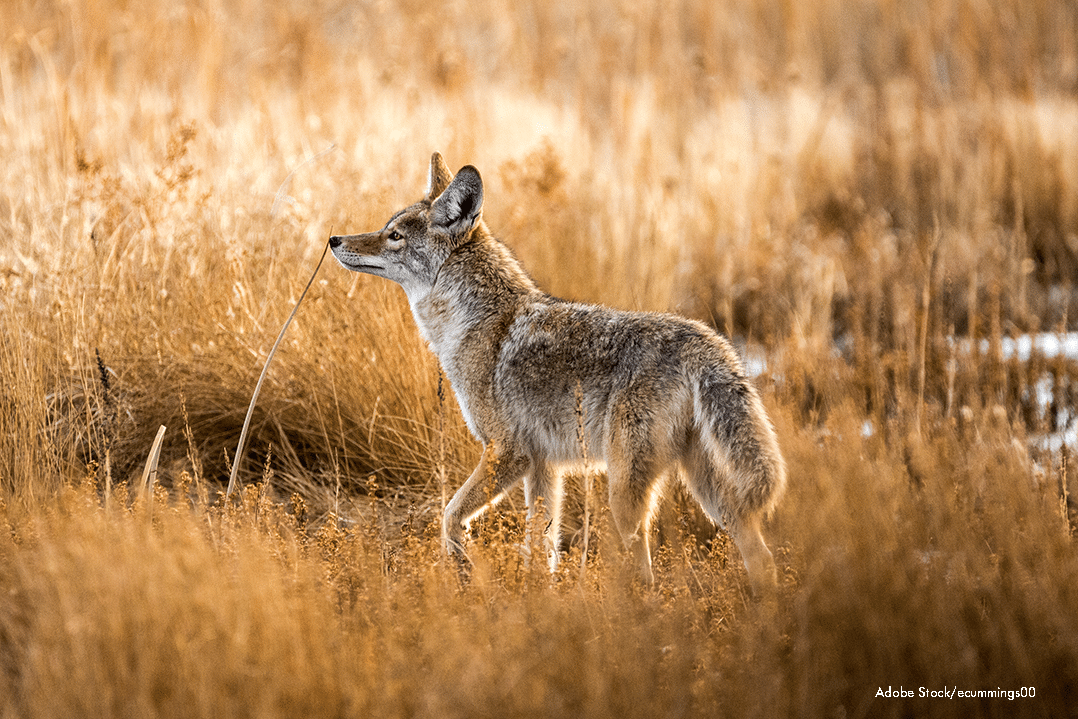
Gray Wolf - Fall
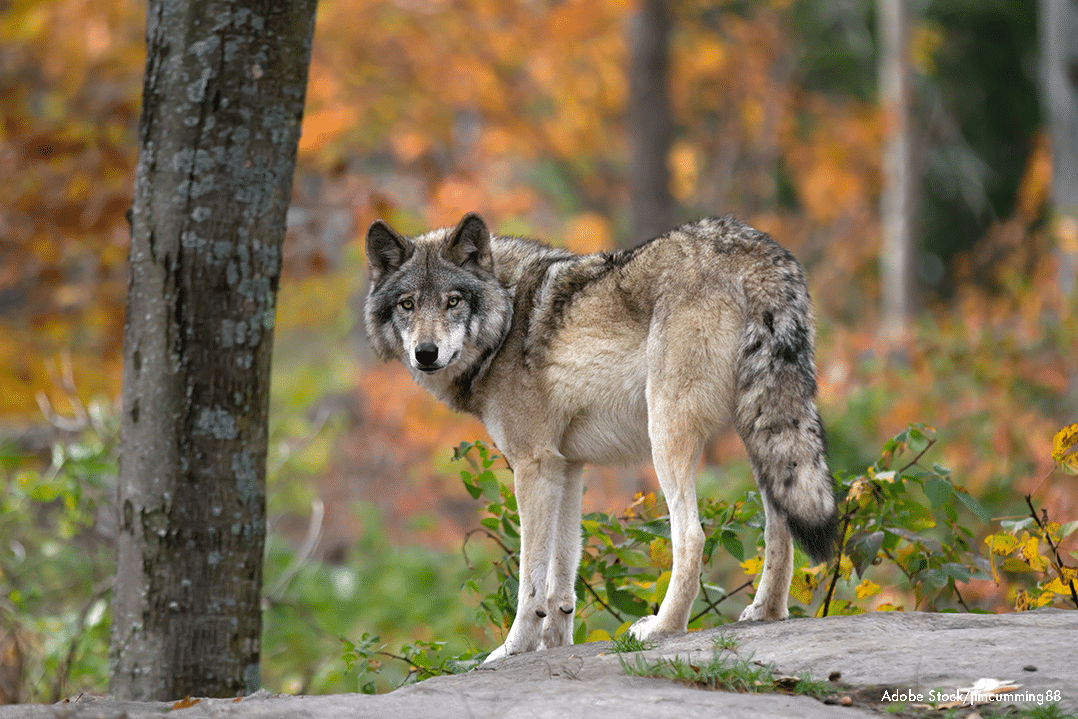

Wild Gray Wolf Caught on Trail Camera - Summer

Wild Gray Wolf Caught on Trail Camera - Winter

Additional Video Resources:
- Two coyotes following a large wolf in Minnesota (VWP)
- Size comparison between coyotes and wolves (VWP)
- Canid ID (IWC)
- Was that wolf? (IWC)
Watch our live streaming Wolf Cams to observe the social dynamics of our ambassador wolves.

The International Wolf Center uses science-based education to teach and inspire the world about wolves, their ecology, and the wolf-human relationship.
